I’d always thought rejecting noise was a key aspect of better Ethernet cables among other things, but as I was looking into capacitance in speaker cables came across this that maintains it’s also a critical factor in digital data transmission. I had no idea and have never seen this discussed before, and I’m thinking this may be yet another reason why pricier Ethernet cables with better design/materials sound better than the cheapies…
Effect of Capacitance on Signal Transmission
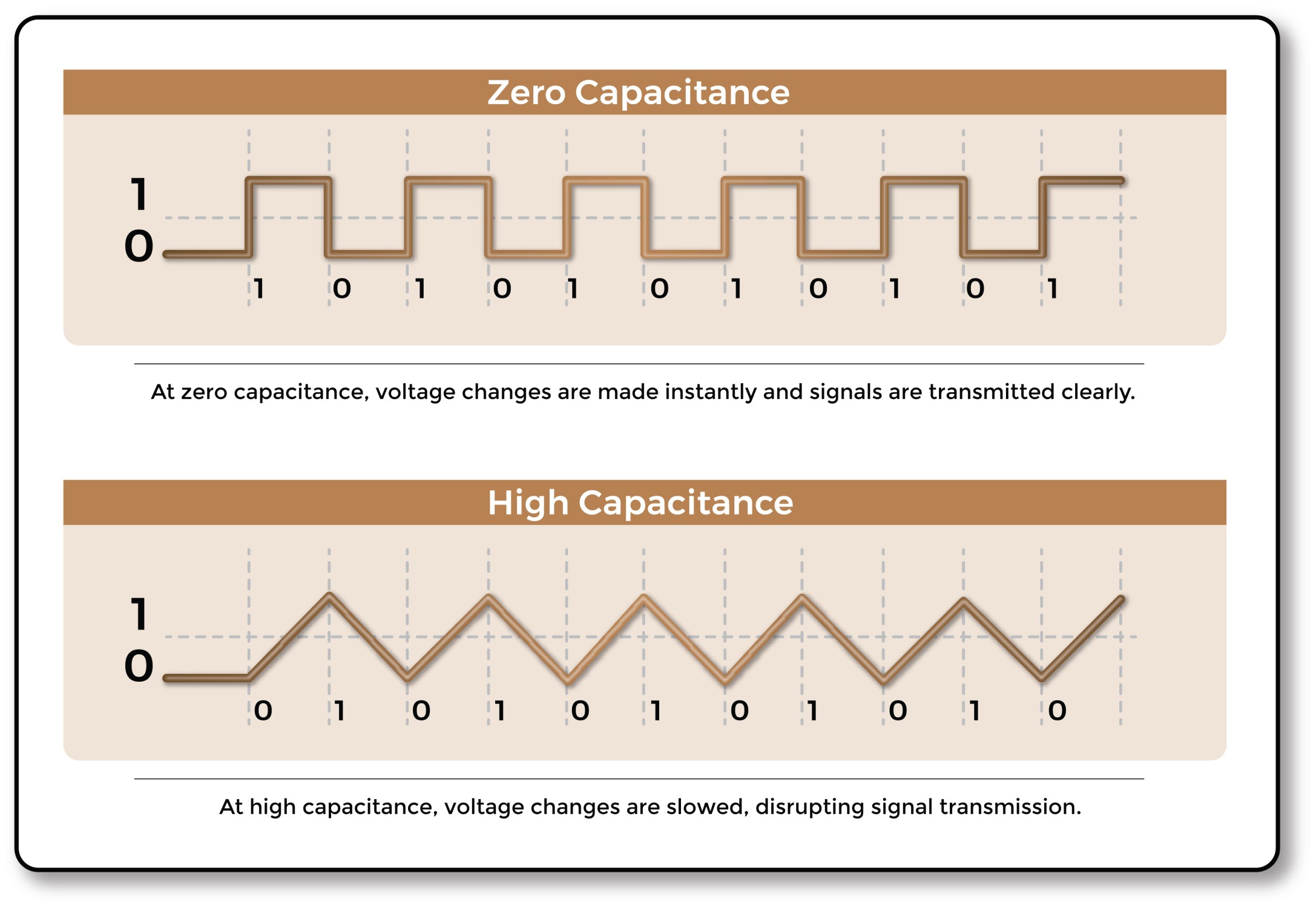
When the voltage applied to conductors changes, the electric field between them charges or discharges in response. However, this does not occur instantaneously, which leads to a delay in voltage change, as well. The higher the capacitance, the slower the voltage change. For signals such as power or simple input/output circuits, the impact is usually negligible. More complex signals, like those transmitted in data networks and building automation communication circuits, can suffer considerably. Excessive capacitance for high-speed data transmission can cause successive bits to bleed into one another and render the signal unrecognizable to the receiver. When this occurs, system malfunction ensues, and inevitably network users and building occupants notice – and loudly voice – their displeasure. An unreliable system using inadequate cable can quickly lead to expensive rewires and damaged dealer reputations.
Designing Cabling for Low Capacitance
Typically, low cable capacitance is considered 15 pF/ft. or less. The total amount of capacitance on an installed cable depends on a variety of factors including cable length, insulation thickness, insulation material, and the presence of shielding. Engineers design data cables with these factors in mind to minimize capacitance and promote clear and undistorted signal transmission.